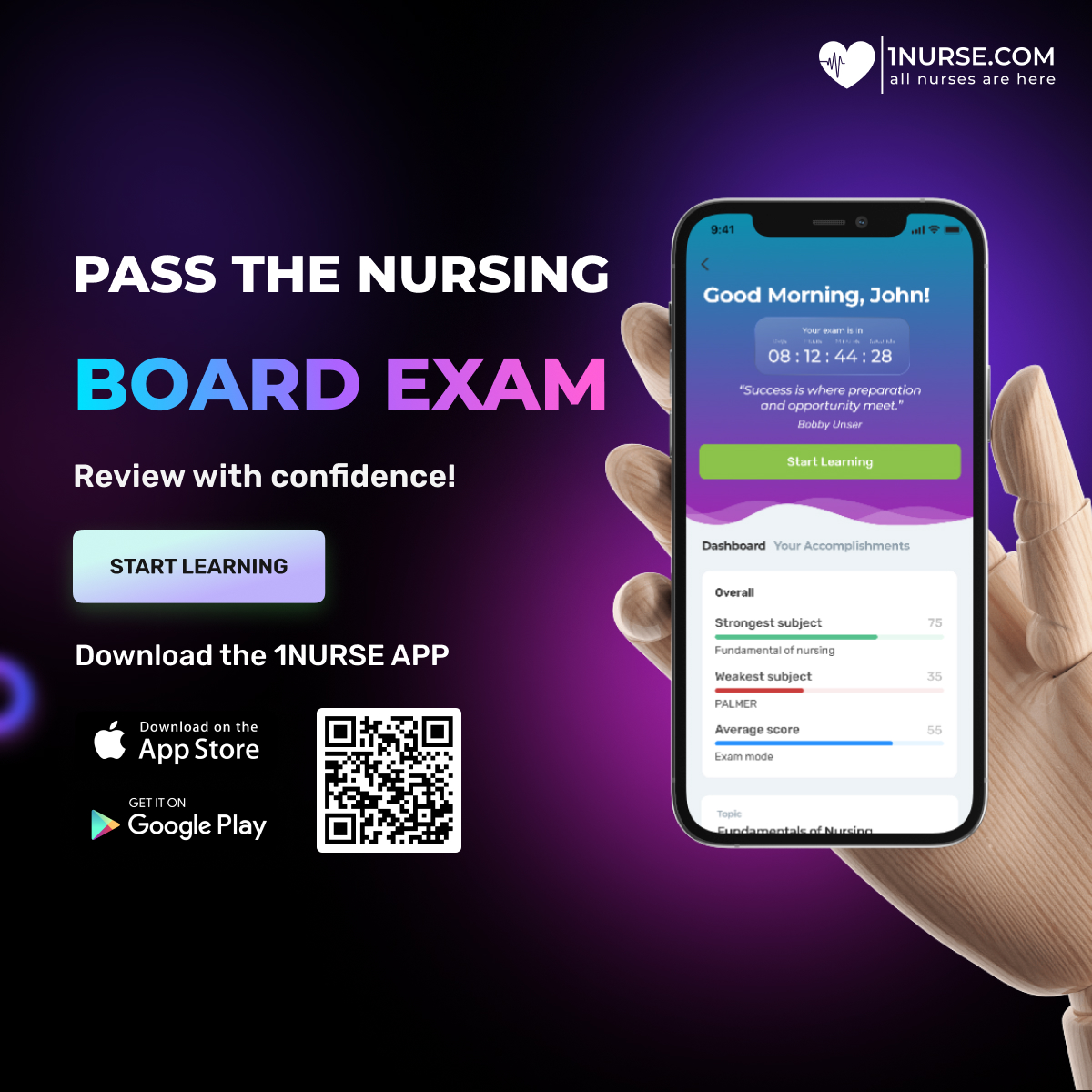
Within the domain of emergency medical services, few positions rival the significance and intensity of the role undertaken by flight nurses. Positioned at the forefront of aeromedical care, these dedicated healthcare providers offer essential critical care and unwavering support to patients during airborne transit, frequently amidst the crucible of high-stress and life-endangering circumstances. In this article, we embark on an exploration of the multifaceted responsibilities, comprehensive training regimens, formidable challenges, and paramount significance held by flight nurses within the contemporary landscape of healthcare systems.
The Role of a Flight Nurse:
A flight nurse, a pivotal member of the medical transport team, is a registered nurse entrusted with the critical task of providing specialized care to patients during aeromedical transport. Operating within the confines of an emergency aircraft, they administer pre-hospital care, drawing upon a repertoire of skills akin to those employed in emergency rooms or intensive care units.
The role of a flight nurse is versatile, adapting to the specific needs of each patient and the dynamics of the transport scenario. Whether collaborating with a flight physician or autonomously managing patient care, their focus remains unwavering on ensuring the safety and well-being of those entrusted to their care.
Flight nurses are integral to both civilian and military medical operations, where they excel in making rapid assessments and formulating dynamic care plans to address the evolving needs of patients. Their expertise extends beyond the confines of traditional healthcare settings, as they navigate the challenges of delivering high-quality care in the confined and often turbulent environment of an aircraft.
In anticipation of transport, flight nurses meticulously devise patient care plans, laying the groundwork for a seamless transition from one location to another. Their proactive approach minimizes disruptions and optimizes the continuity of care, thereby enhancing patient outcomes and fostering a sense of reassurance amidst the chaos of medical emergencies.
Responsibilities:
The responsibilities of flight nurses encompass a wide range of medical and logistical tasks, including:
Patient Assessment and Care: Flight nurses must quickly assess a patient's condition and provide appropriate medical care, including administering medications, monitoring vital signs, and performing emergency procedures as needed.
Stabilization: In many cases, flight nurses are tasked with stabilizing critically ill or injured patients before and during transport. This may involve managing airway and breathing, controlling bleeding, and providing interventions to prevent further deterioration.
Communication: Effective communication is crucial in the fast-paced environment of aeromedical transport. Flight nurses must liaise with other members of the medical team, pilots, and ground personnel to ensure smooth coordination and transfer of patients.
Equipment Management: Flight nurses are responsible for ensuring that all medical equipment and supplies are properly stocked and functioning during flights. This includes advanced medical devices such as ventilators, cardiac monitors, and infusion pumps.
Documentation: Accurate documentation of patient assessments, interventions, and vital signs is essential for continuity of care. Flight nurses must maintain detailed records of their actions during transport for the patient's medical records and handover to receiving medical facilities.
Training and Qualifications:
Becoming a flight nurse requires a strong foundation in nursing combined with specialized training in aeromedical transport. The typical path involves:
Registered Nurse (RN) Licensure: Flight nurses must first obtain licensure as registered nurses by completing a nursing program and passing the NCLEX-RN examination.
Clinical Experience: Prior experience in critical care, emergency medicine, or trauma nursing is highly beneficial for aspiring flight nurses. Many employers require a minimum of two to three years of experience in these settings.
Advanced Certifications: Flight nurses often pursue advanced certifications such as Certified Flight Registered Nurse (CFRN) or Critical Care Registered Nurse (CCRN) to demonstrate proficiency in aeromedical transport and critical care nursing.
Aeromedical Training: Specialized training in aeromedical transport is essential for flight nurses to safely and effectively perform their duties. This training covers topics such as aviation physiology, patient loading and securing, and in-flight medical management.
Challenges:
Flight nursing is not without its challenges, as it involves working in dynamic and unpredictable environments with limited resources. Some of the key challenges faced by flight nurses include:
High-Stress Situations: Flight nurses must remain calm and focused under pressure, often dealing with critically ill or injured patients in challenging conditions such as adverse weather or remote locations.
Resource Limitations: Aeromedical transport often involves working with limited space, equipment, and medical supplies. Flight nurses must be resourceful and adaptable in improvising solutions to overcome these limitations.
Risk of Injuries: Working in helicopters or other aircraft carries inherent risks, including turbulence, crashes, and exposure to extreme weather conditions. Flight nurses must adhere to strict safety protocols and undergo regular training to mitigate these risks.
Emotional Toll: Witnessing traumatic injuries and dealing with life-and-death situations can take a toll on the mental and emotional well-being of flight nurses. Support systems and debriefing sessions are essential for addressing these challenges and preventing burnout.
Importance in Healthcare:
Flight nurses play a crucial role in the healthcare system by ensuring timely access to advanced medical care for critically ill or injured patients, especially in remote or underserved areas. Their ability to deliver specialized medical interventions during air transport can significantly improve patient outcomes and survival rates. Additionally, flight nurses serve as liaisons between pre-hospital and hospital-based care teams, facilitating seamless transitions and continuity of care for patients.
Flight nursing is a demanding yet rewarding profession that requires a unique blend of clinical expertise, critical thinking, and resilience. These unsung heroes of the skies play a vital role in providing life-saving care to patients during aeromedical transport, often in challenging and high-stakes situations. As technology advances and healthcare systems evolve, the importance of flight nurses in delivering specialized medical care will only continue to grow, ensuring that patients receive the critical care they need, wherever they may be.
Photo Source : Freepik